Introduction
The Pillars of Islam are the fundamental basis of worship mandated upon every mukallaf, an individual who has reached the capacity to bear religious responsibilities. Starting with the declaration of the two testimonies of faith as the first pillar, each subsequent pillar of Islam distinguishes a Muslim from a non-believer.
A Muslim, by definition, is one who surrenders their soul and body solely to Allah and obeys all His commands and prohibitions.
A Muslim who performs their prayers perfectly will certainly stand out from their non-Muslim peers. Similarly, the act of fasting signifies this distinction. If a Muslim neglects fasting during Ramadan, their appearance would resemble that of disbelievers, creating a lack of discernible difference between them and non-believers.
The Pillars of Islam are five fundamental principles that guide every Muslim’s life. They not only signify a servant’s obedience to their Lord but also shape their character, discipline, and personality.
Below are the pillars:
1. Declaration of the Two Testimonies of Faith
أشهد أن لا إله إلا الله.وأشهد أن محمداً رسول الله
“I bear witness that there is no God but Allah, and I bear witness that Muhammad is the Messenger of Allah.”
These two phrases constitute the declaration of faith that confirms one as a Muslim. They are not merely verbal affirmations but heartfelt confessions accompanied by actions. This declaration requires belief in the oneness of Allah (Tawhid) and adherence to the teachings of Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) as the conveyor of revelation.
When this confession originates from the heart, merely uttering it with the lips carries no significance if one does not comprehend its meaning. For instance, if a disbeliever is coerced to recite this declaration under duress, their conversion to Islam is invalid.
Similarly, if someone is tricked (e.g., as part of a prank) into reciting it in exchange for receiving an iPhone without understanding its meaning, they also do not become a Muslim.
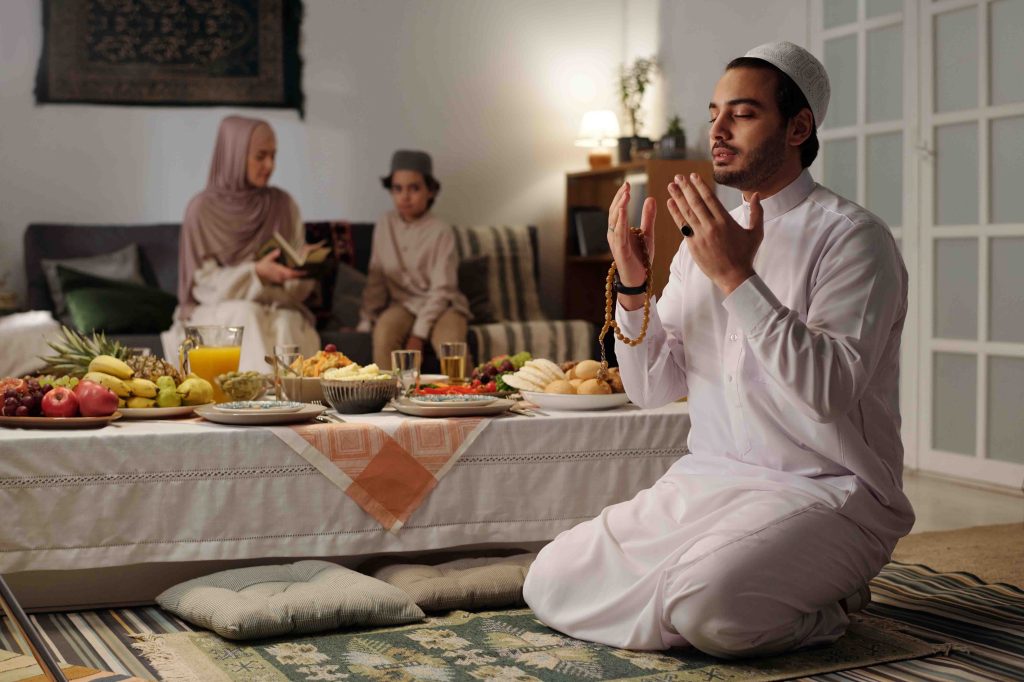
2. Salah (Prayer)
Prayer is a daily act of worship performed five times a day, including Fajr, Dhuhr, Asr, Maghrib, and Isha. Salah connects a Muslim with Allah, strengthens spiritual ties, and fosters self-discipline.
If a Muslim performs their prayers but their behavior and lifestyle fail to reflect noble character, it may indicate deficiencies in their prayer or that their prayer is not being accepted.
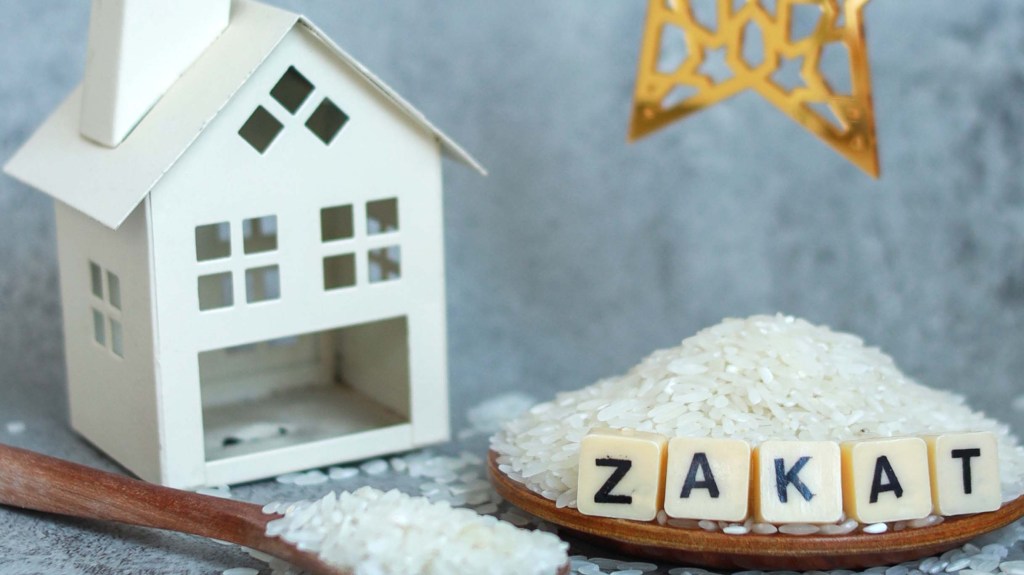
3. Zakat (Obligatory Charity)
Zakat is an obligation to give a small portion of one’s wealth to those in need. It aims to assist the poor, eradicate poverty, and strengthen solidarity within the Muslim community.
4. Sawm (Fasting)
Fasting is observed throughout the month of Ramadan, during which Muslims abstain from eating, drinking, and invalidating acts from dawn until sunset. Fasting not only cultivates patience but also enhances spiritual awareness and empathy for the less fortunate.
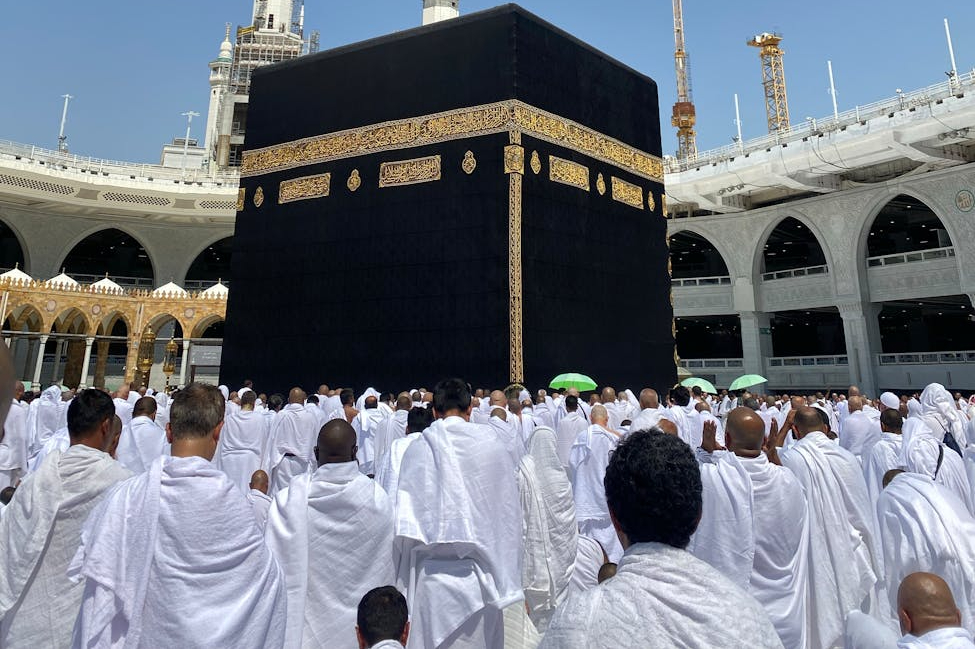
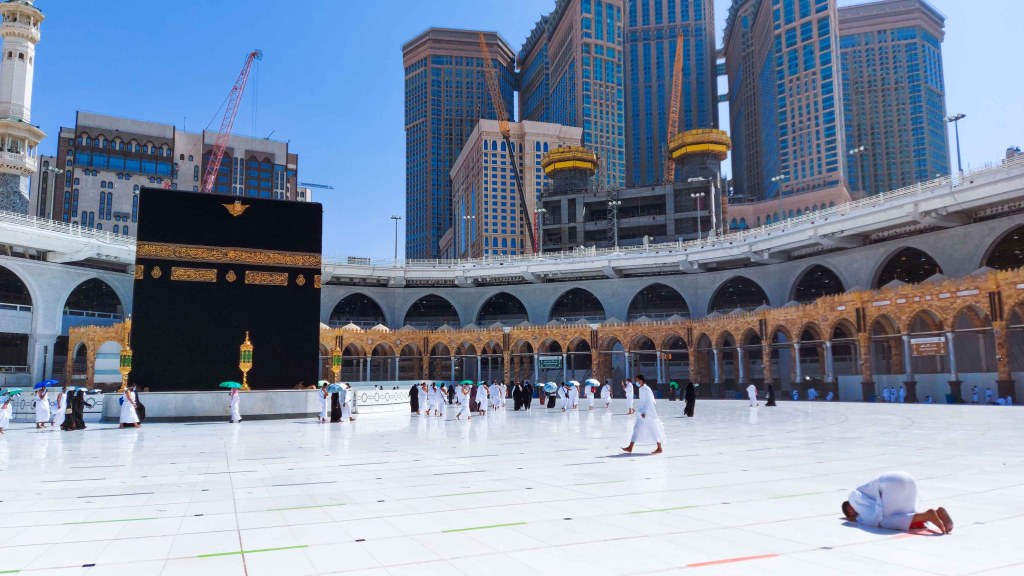
5. Hajj (Pilgrimage to Mecca)
Hajj is the final pillar of Islam, obligatory for those who are financially and physically capable. It is performed once in a lifetime. This journey strengthens Islamic unity and reminds Muslims of equality before Allah.
Conclusion
The Pillars of Islam form the foundation of a Muslim’s faith and practices. Through understanding and implementing these five pillars, Muslims can achieve a balance between worldly life and the hereafter, becoming individuals who contribute positively to society. A Muslim who adheres to the Pillars of Islam will exhibit clear differences from non-Muslims in terms of character, discipline, and commitment to fulfilling life’s responsibilities. Learn and embody these pillars to shape a blessed life.