Introduction
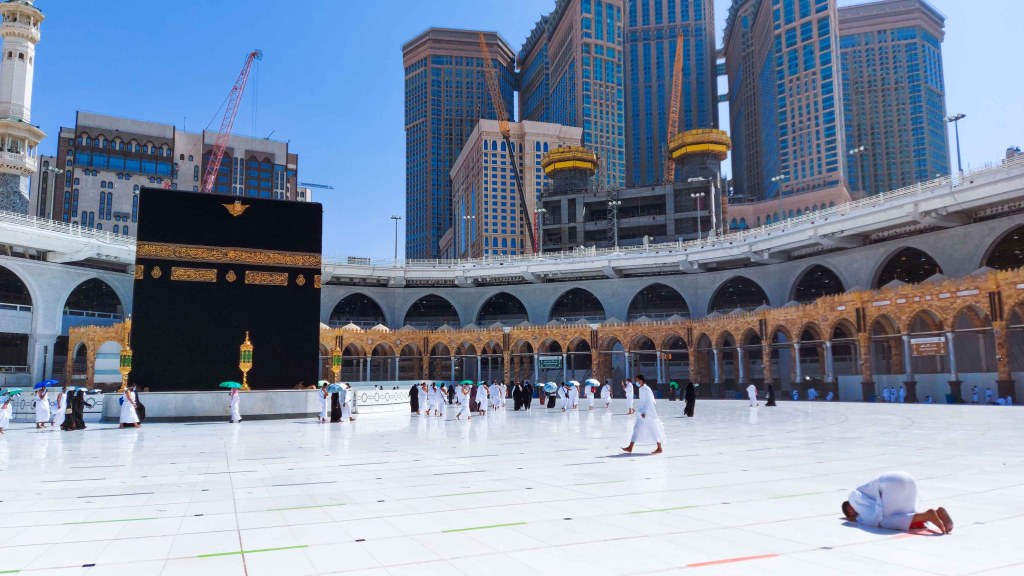
Hajj is the fifth pillar of Islam and represents the pinnacle of worship in the life of a Muslim. It is an obligatory act to be performed once in a lifetime for those who are physically, financially, and safely able to do so, as stated in Surah Ali Imran, verse 97:
Surah Ali Imran, verse 97
“And [due] to Allah from the people is a pilgrimage to the House—for whoever is able to find thereto a way.”
The History of Hajj
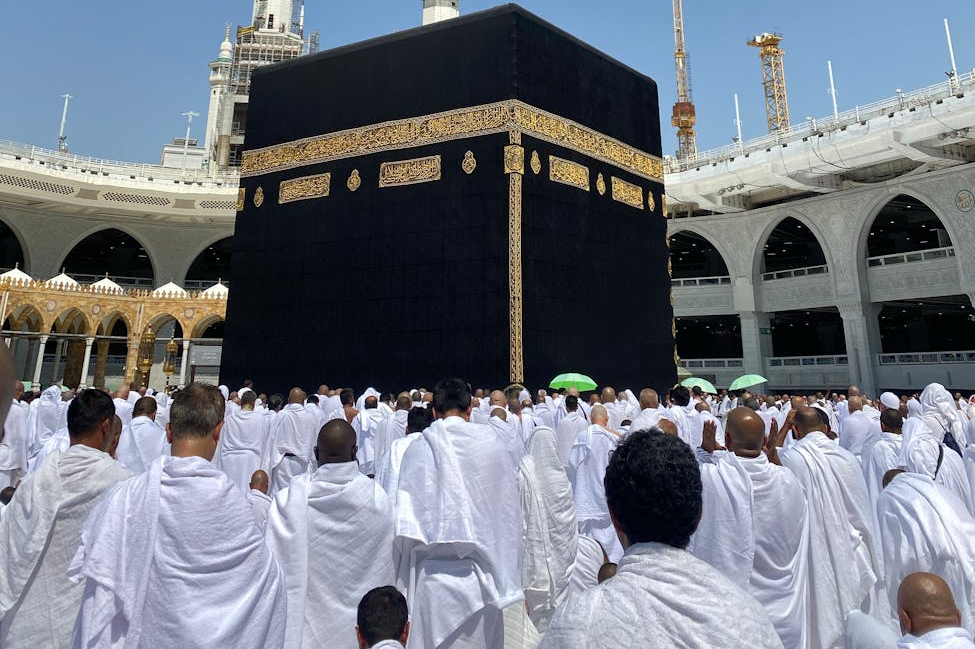
The pilgrimage began during the time of Prophet Ibrahim (Abraham, AS), when Allah commanded him and his son, Prophet Ismail (Ishmael, AS), to build the Kaaba in Mecca as a house of worship for humanity. In Surah Al-Hajj, verse 27, Allah says:
Surah Al-Hajj, verse 27
“And proclaim to the people the Hajj [pilgrimage]; they will come to you on foot and on every lean camel; they will come from every distant pass.”
Since then, Hajj has been a significant symbol of Islam. Prophet Muhammad SAW later completed the rituals of Hajj and set guidelines for it, known as the Farewell Pilgrimage (Hajjatul Wada’) in the 10th year of Hijrah. This journey became the foundation of the Hajj as practiced by Muslims today.
The Merits of Hajj
Cleansing of Sins
Prophet Muhammad SAW said:
“Whoever performs Hajj without committing obscenity or transgression will return as free from sins as the day his mother gave birth to him.”
(Sahih al-Bukhari and Sahih Muslim) [1]
Strengthening the Bond with Allah
Hajj signifies total submission to Allah. Every ritual, such as tawaf (circumambulation), sa’i (walking between Safa and Marwah), and wuquf (standing) in Arafat, reflects obedience to Allah’s commands.
Unity of the Muslim Ummah
Hajj gathers Muslims from various races, skin colors, and languages in one place, demonstrating the unity of Islam that transcends worldly boundaries.
Hajj and Its Connection to the Pillars of Faith
Belief in Allah: Hajj is a devotion that requires complete faith in Allah.
Belief in the Hereafter: Rituals like wuquf in Arafat remind Muslims of the Day of Judgment.
Belief in the Scriptures: The guidance for performing Hajj is outlined in the Quran and Sunnah.
Belief in the Prophets: Prophet Ibrahim AS and Prophet Muhammad SAW serve as exemplary figures in the performance of Hajj.
The Wisdom of Performing Hajj
Enhancing Taqwa (Piety): Hajj trains Muslims to refrain from prohibited acts during ihram and to uphold worship.
Increasing Patience: Facing crowds and challenges during Hajj cultivates patience.
Reflecting on Life’s Purpose: Hajj provides an opportunity to reflect on past sins and strive for self-improvement.
Conclusion
Hajj is not merely an obligation but a spiritual journey that strengthens faith in Allah and belief in the Hereafter. It manifests the pillars of faith in a Muslim’s life, renewing their connection with Allah, trusting His promises in the afterlife, and emulating the examples of the prophets. May we all be granted the ability to fulfill this sacred call and attain Allah’s pleasure. Ameen.
Fundamentals of Believe | Pillars of Faith | Pillars of Islam | Al-Quran | History
References
- Sunnah.com. (n.d.). Sahih al-Bukhari 1521 – The Book of Hajj. Retrieved December 25, 2024, from https://sunnah.com/bukhari:1521